Depatment of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tago lab
Research
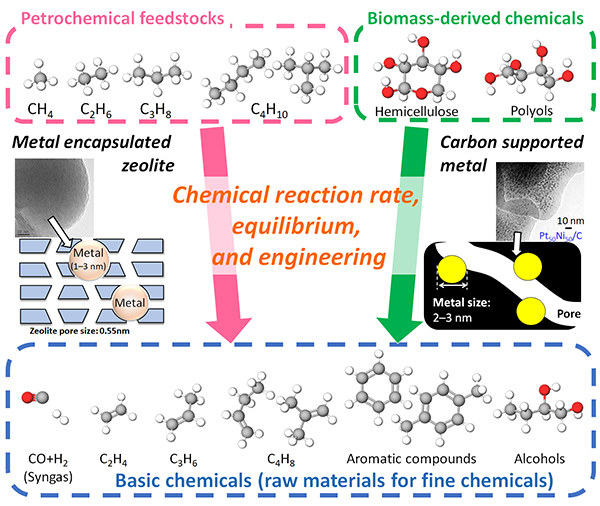
Our laboratory is working on
(1) improving the efficiency of petrochemical processes;
(2) developing catalytic reaction prosesses; and
(3) utilizing biomass-related materials effectively
through the development and design of catalyst materials and processes based on catalytic reaction engineering.
[Research topics]
(1) Development of metal nanoparticle catalyst encapsulated in zeolite (Birdcage-type zeolite)
(2) Carbon supported metal nanoparticle catalysts for hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions
(3) Evaluation of catalytic structure and funtions of metal-oxide complex catalysts based on kinetic analysis
(1) Development of metal nanoparticle catalyst encapsulated in zeolite (Birdcage-type zeolite)
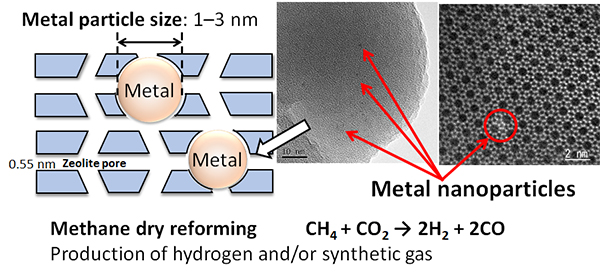
Zeolite is crystalline porous materials with pores of less than 1 nm (1 nm=10-9 m). We are developing a Birdcage-type zeolite catalyst that encapsulates matal ultrafine particles with a particle size of several nanometers in zeolite crystals.
In this structure, metal particles are immobilized in the zeolite crystal and thus high catalytic activity and excellent tharmal stability are expected.
[Applications]
・ Effective utilization of carbon dioxide and hydrogen production
[Papers]
Chem. Eng. J., 377 (2019) 120203.
・Synthesis of C2-C4 olefins and aromatics
[Papers]
Catal. Today, in press (2020).
(2) Carbon supported metal nanoparticle catalysts for hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions
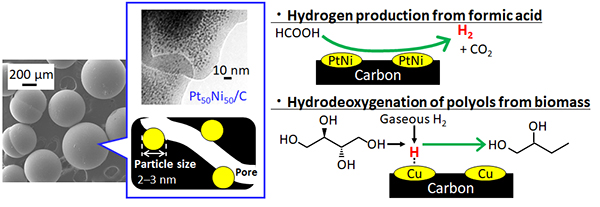
Carbon supports are expected to be able to perform the target reaction selectively because there are no active sites that can cause side reactions. However, when metal is loaded on carbon support, the metal particles become larger and the catalytic activity decreases.
In contrast, we are developing catalysts in which metal ultrafine particles with diameters ranging from 1 to 3 nm (1 nm=10-9 m) are embedded in porous carbon using ion-exchange resin with metal ions (Pt, Ni, Pd, and so on) as precursors.
[Applications]
・ High efficient hydrogen production
[Papers]
Chem. Eng. J., 377 (2019) 120276.
J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 52(5) (2019) 423-429.
・Biomass conversion
[Papers]
Appl. Catal. A: Gen, 619 (2021) 118152.
(3) Evaluation of catalytic structure and funtions of metal-oxide complex catalysts based on kinetic analysis
The partial oxidation of olefins is one of the most important reactions in the petrochemical process.We are developing higher performance catalyst structure and preparation method for complex oxide catalysts consisting of Co, Bi, and Mo, which are highly active in partial oxidation. To achieve this, we are investigating the relationship between catalytic structure and activity from the analysis of physical and chemical properties and reaction kinetics.
Contact info.
Mailing address:
S1 bldg. #304 and #305
2-12-1, Ookayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, 152-8552, Japan
Phone: +81-3-5734-2115,2629